A Four-Year Institutional Experience of Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction
Rosie Friedman, Melisa Granoff, Aaron Fleishman, Kathy Shillue, Anna Rose Johnson, Bernard Lee, Ted James, Dhruv Singhal
Dept of Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States
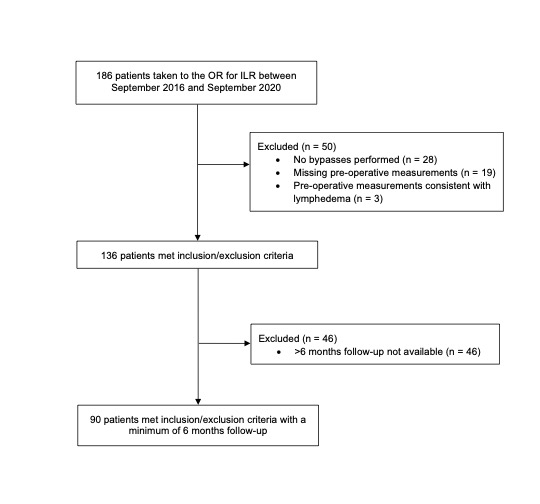
Objective(s): Up to 1 in 3 patients may go on to develop breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) after treatment. Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction (ILR) is a surgical procedure that has been shown in early studies to reduce the risk of BCRL. However, long-term outcomes are limited due to its recent introduction and different institutions' eligibility requirements. This study evaluates the incidence of BCRL in a cohort that underwent ILR over the long-term. Design: A retrospective review was performed. Setting: A review was conducted of all patients referred for ILR at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center from September 2016 through September 2020. Patients: Breast cancer patients who underwent ILR with preoperative measurements, a minimum 6-months follow-up data and at least one completed lymphovenous bypass were identified. Interventions: Patients underwent immediate lymphatic reconstruction at the time of axially lymph node dissection. Main Outcome Measure(s): Medical records were reviewed for demographics, cancer treatment data, intra-operative management and lymphedema incidence. Results: A total of 186 patients with unilateral node-positive breast cancer underwent axillary nodal surgery and attempt at ILR over the study period. Ninety patients underwent successful ILR and met all eligibility criteria, with a mean patient age of 54 years and median BMI of 26.6 kg/m2. Median number of lymph nodes removed was 14. Median follow-up was 17 months (range: 6-49). 87% of patients underwent adjuvant radiotherapy of which 97% received regional lymph node radiation. At the end of the study period, we found an overall 9% rate of LE. Conclusion: Utilizing strict follow-up guidelines over the long-term, our findings support ILR at time of axillary lymph node dissection is an effective procedure that reduces the risk of BCRL in a high-risk patient population.
Back to 2022 Posters
