A Bariatric Surgery Derived Gut Metabolite is a Potent Single and Combination Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (T2D)
Andrei Moscalu1, Yingjia Chen1, Snehal N. Chaudhari2, Renuka Haridas3, James N. Luo1, Cullen F. Roberts1, Mehran Karvar1, Ali Tavakkoli1, Sloan A. Devlin2, Eric Sheu1
1Surgery, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States, 2Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United States, 3Affinivax, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States
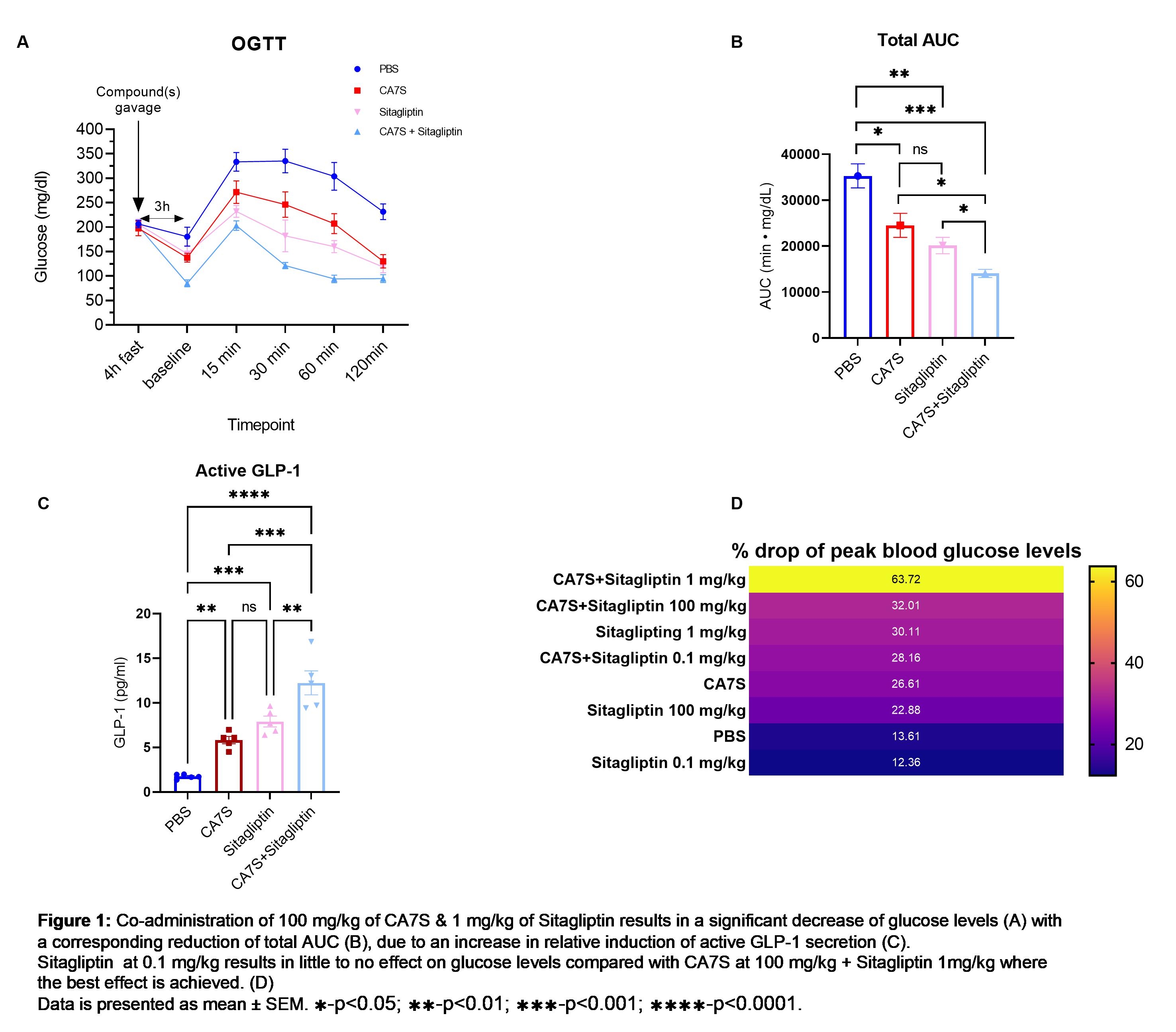
1. Objective. The present study aimed to investigate, in a murine model, the antidiabetic efficacy of cholic-acid-7-sulfate (CA7S) alone or in combination with sitagliptin. CA7S is a gut-restricted metabolite that is upregulated by sleeve gastrectomy in both mice and humans. CA7S lowers blood glucose by inducing glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion in the gut. Thus, CA7S is a potential oral GLP-1 based T2D therapy, unlike most GLP-1 analogues today. Sitagliptin is an approved T2D drug that prolongs GLP-1 half-life by inhibiting its degradation.
2. Design. Experimental animal study.
3. Setting. Experimental animal laboratory.
4. Participants. 100, 16-week-old male, diet-induced-obese, insulin-resistant C57BL/6J-mice, weight and fasted-glucose matched before any intervention.
5. Interventions. Mice were split in 4 groups and received PBS, CA7S (100 mg/kg), sitagliptin, or CA7S (100 mg/kg) + sitagliptin. An incremental dose of sitagliptin was used: 0.1, 1 and 100 mg/kg. Fasted mice were orally-gavaged with the indicated compound(s), and 3-hours later, were subjected to an oral-glucose-tolerance-test (OGTT). Active serum GLP-1 levels were also measured 15 minutes after glucose administration.
6. Main Outcome Measure(s). The antidiabetic efficacy of CA7S alone or in combination with sitagliptin.
7. Results. CA7S alone reduces peak blood glucose levels (p-BGL) by 26.6% (p<0.01) decreasing the total-area under the curve (t-AUC) by 30.5% (p<0.05) when compared to control (PBS). A similar effect is seen after 1mg/kg of sitagliptin (p<0.01). Co-administration of CA7S and sitagliptin drops p-BGL by 63.7% and t-AUC by 60.1% (p<0.001, Fig.1A-D). GLP-1 increases by 233% after CA7S, p<0.01; 352% after 1mg/kg of Sitagliptin (p<0.001) and 600% after the combination of the two (p<0.0001) when compared with control (Fig.1E).
8. Conclusions. Single and combination therapy of CA7S, a surgically induced, gut-restricted metabolite and sitagliptin, improves glucose tolerance and augments GLP-1 secretion.
Back to 2022 Abstracts
