Duodenal switch and single anastomosis duodeno-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity: a single institution experience
Piyush Gupta, Brett Baker, Tiare Pimentel, Sara Tortorici, Dmitry Nepomnayshy, Heather Ford, Thomas Schnelldorfer, Reuben Shin, David M. Brams
General Surgery, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Burlington, Massachusetts, United States
Objective: Single institutional experience with laparoscopic duodenal switch (DS) and single anastomosis duodeno-ileal bypass (SADI-S) and provide comparisons of long-term weight loss and resolution of comorbidities.
Design: Retrospective chart review of 29 patients who underwent DS or SADI-S from 2014 through 2021.
Setting: Tertiary-care, academic teaching hospital.
Patients: All patients who underwent DS or SADI-S from 2014-2021.
Interventions: Laparoscopic DS or laparoscopic SADI-S
Main Outcome Measures: Weight loss expressed as percent excess body weight loss needed to achieve a body mass index of 23, resolution of obesity-related comorbidities
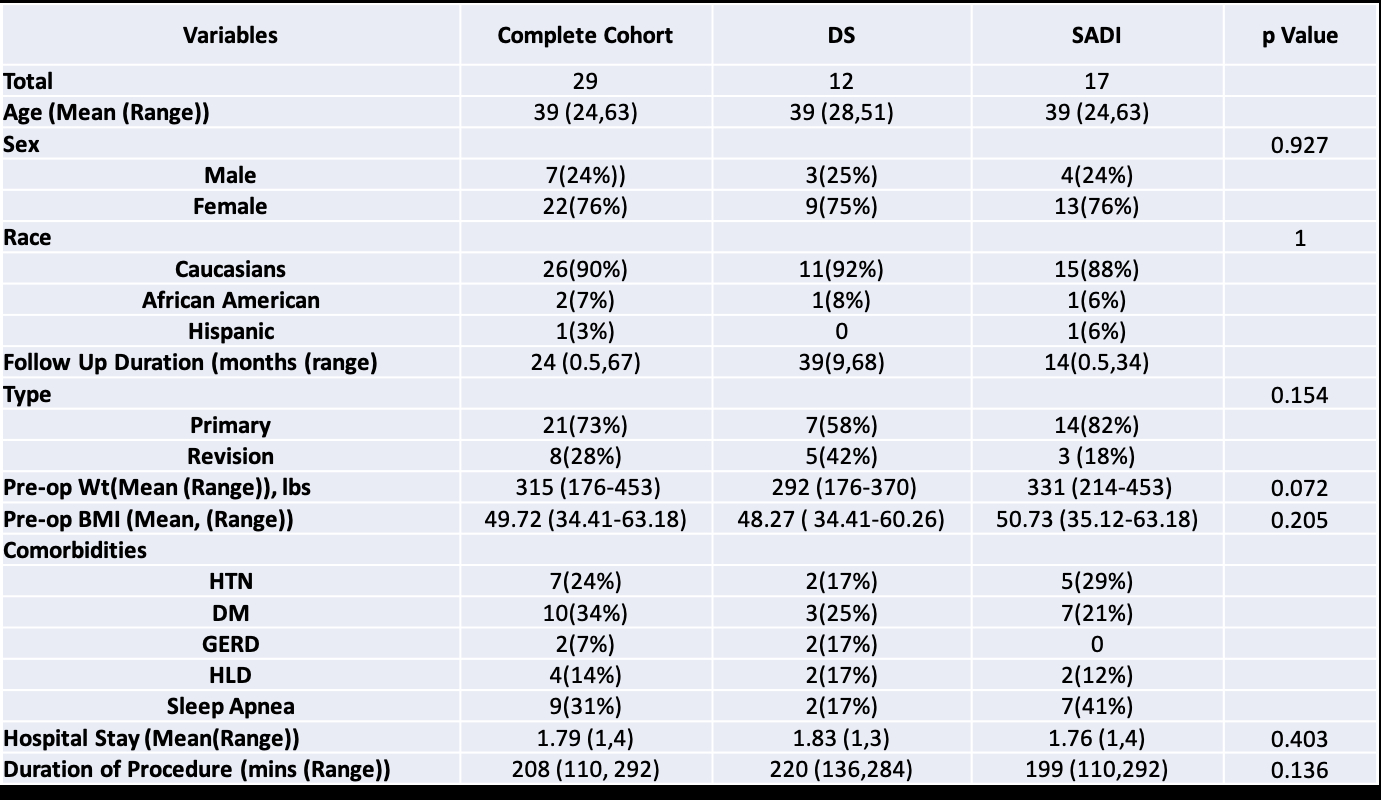
Results: 12 patients underwent DS, 7 primary procedures, 4 conversions from sleeve gastrectomy, and 1 conversion from Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. 17 patients underwent SADI-S, 14 primary procedures, and 3 conversions from prior sleeve gastrectomy. Baseline demographics, preoperative BMI, and obesity-related comorbidities were comparable between the two groups (Fig 1). Percent excess body weight loss was similar in both primary and conversion cases and overall at 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years were 43.1%, 53.1%, and 53.4%, respectively. Of note, weight loss was maintained at 3-5 years in patients with long-term follow-up. Comorbidity resolution was noted across the spectrum of disease, with a statistically significant reduction in hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Univariate regression analysis showed BMI >50 and absence of preoperative hypertension were statistically significant positive predictors of higher EBWL at 2 years.
Conclusions: Both duodenal switch and SADI-S are effective at enabling durable weight loss beyond two years with statistically significant resolution of comorbidities. Notably, weight loss trends after conversion from sleeve to SADI are early evidence that a staged procedure may be equally effective.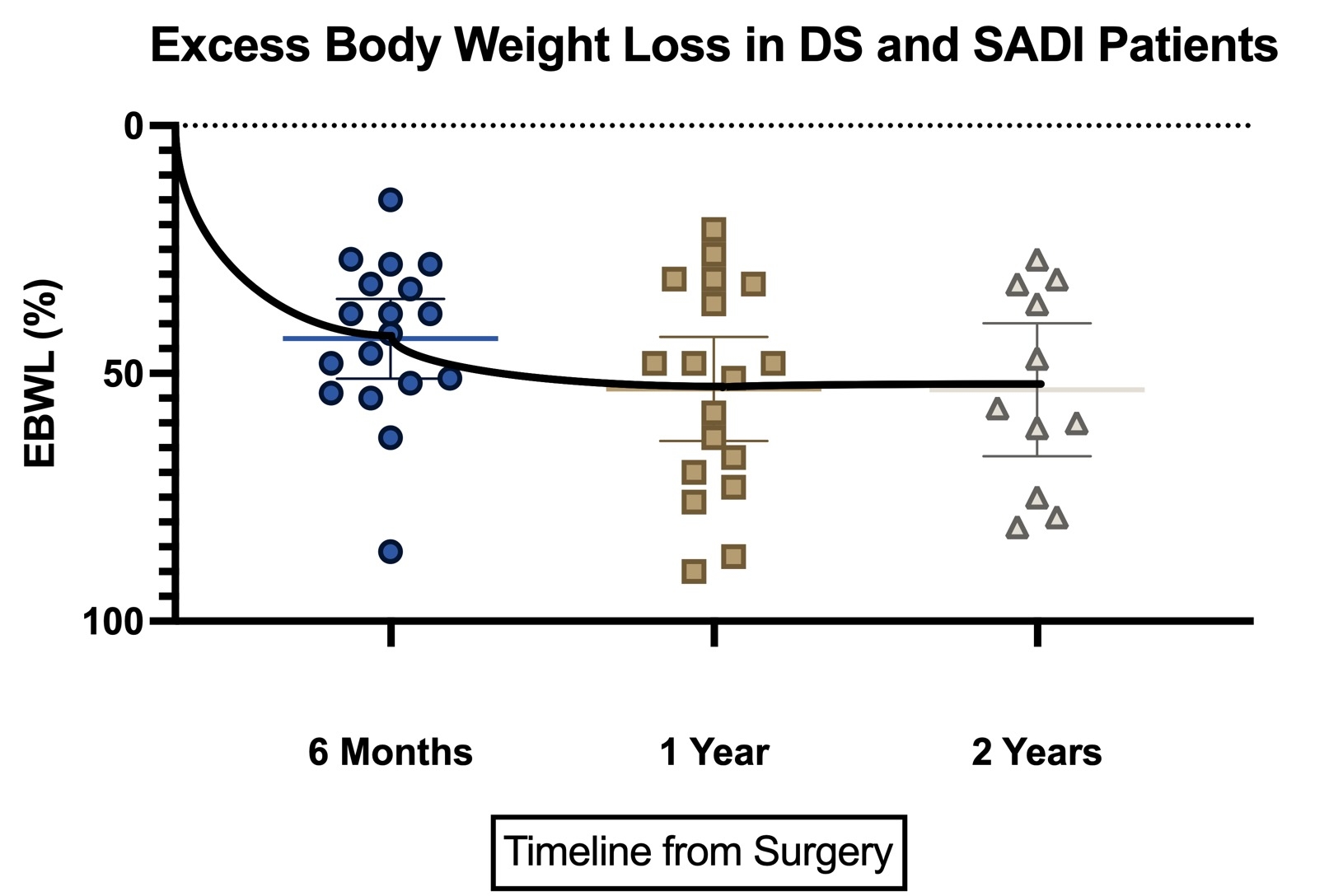
Back to 2021 Posters
