Human Myeloid Cell Infiltration In Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Is Increased in FLT3 Ligand Knockout Humanized Mice
Hannah Buettner1, Jane Chuprin1, Michael Brehm1, Giles F. Whalen2
1Molecular Biology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, United States, 2Surgery, University of Massachusetts Memorial Medical Center, Worcester, Massachusetts, United States
OBJECTIVE: There is a need for preclinical models which faithfully recapitulate the tumor immune microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
There is a growing body of evidence implicating myeloid cells in the mechanism of resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy, however, prior humanized mouse models have had limited development of human myeloid cells. The recently developed FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) ligand knockout mice have greater levels of human myeloid cell engraftment; we hypothesized that patient derived xenograft (PDX) PDAC tumors grown in FLT3 mice would have increased intratumoral human myeloid cell infiltration.
METHODS: PDX PDAC tumors were implanted subcutaneously in FLT-3 and NOD-scid IL2rgnull (NSG) mice engrafted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Flow cytometry was performed to confirm engraftment, and humanized mice were sacrificed when tumors were >300 mm3. Immunohistochemistry staining of PDAC tumor samples was performed for human CD45, and human CD68 was used as a myeloid marker.
RESULTS: PDX PDAC tumors from both NSG and FLT-3 mice had similar levels and distribution of cells staining positive for human CD45, however, PDX PDAC tumors from FLT-3 mice had increased staining for human CD68 compared with those from NSG mice (fig. 2).
CONCLUSIONS: In keeping with previous studies which have shown increased human myeloid cell engraftment in FLT-3 humanized mice as compared with NSG, we have demonstrated increased human myeloid cell presence in PDX PDAC tumors in FLT-3 humanized mice. This suggests the FLT-3 model may more faithfully recapitulate the human immune tumor microenvironment and thus serve be a useful model for development and evaluation of novel therapies for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.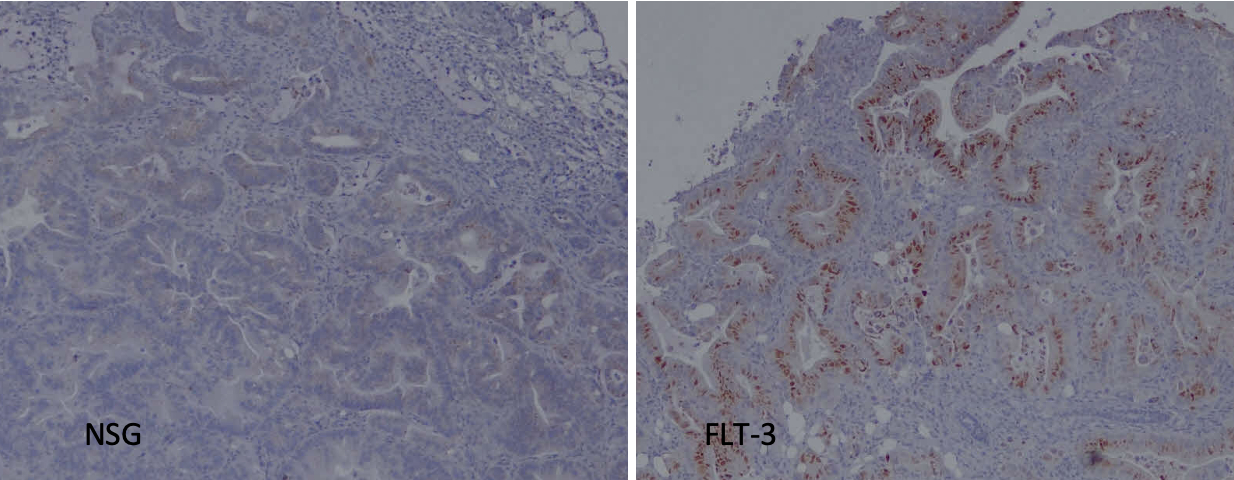
Back to 2021 Posters
