Routine Blood Count Monitoring is Unnecessary After Uncomplicated Appendectomy
Eleah D. Porter1, *Lye-Yeng Wong2, *Allison R. Wilcox1, Jenaya L. Goldwag1, *Spencer W. Trooboff1, Eric D. Martin1,2, *Alexandra Briggs1,2, Christina V. Angeles1,2, *Andrea B. Wolffing1,2
1Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH;2Geisel School of Medicine, Hanover, NH
Objective: Laboratory tests are often obtained empirically post-surgery without specific indications. Our goal was to assess the incidence and utility of routine blood count (BC) monitoring in adults after appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis.
Design: Retrospective cohort study of patients undergoing routine (no documented clinical indication or concern) BC monitoring (CBC or H&H lab) within 24 hours of surgery.
Setting: Academic quaternary care center.
Patients: Adult patients post-appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis (simple or suppurative) from 2013-2018.
Interventions: N/A
Main Outcome Measures: 1. Lab driven change in clinical care 2. 30-day mortality, readmission and intra-abdominal/pelvic abscess formation.
Results: Over the study period, 319 patients met inclusion criteria. Routine BC monitoring labs were obtained on 42% (134/319) of patients, of which 89% (119/134) had an abnormality by institutional lab thresholds. Lab results prompted a change in care in only 3% (4/134) of tested patients (Figure 1). On univariate analysis, patients undergoing routine BC monitoring were significantly older, had more comorbidities and had an ASA class ≥3 (all p<0.001) compared to those not tested. Routine BC monitoring was also associated with suppurative appendicitis (p=0.007), open surgery (p<0.001) and higher blood loss (p<0.001). There were no differences in 30-day mortality, readmission or post-operative intra-abdominal/pelvic abscess between those who did and did not undergo routine BC monitoring.
Conclusions: Routine post-appendectomy BC monitoring does not impact clinical care or outcomes in adults with uncomplicated appendicitis. Quality initiatives should be pursued to decrease utilization of empiric laboratory testing and reserve use for patients with specific post-operative clinical concerns. 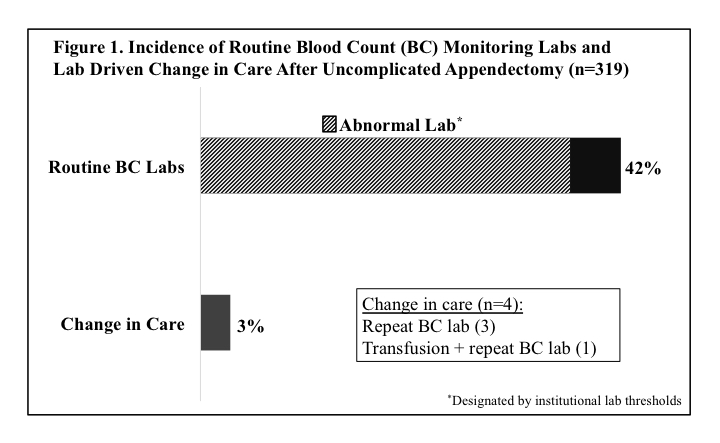
Back to 2019 Posters




