Evolving Multimodality Treatment Strategies in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
*Abby White1, *Suden Kucukak1, *Daniel N. Lee1, *Emily Polhemus1, *Emanuele Mazzola2, Michael Jaklitsch1, *Steven Mentzer1, *Jon Wee1, *Raphael Bueno1, Scott J. Swanson1
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA;2Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA
Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of surgery, with and without induction therapy, in locally advanced (Stage IIIA) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Design: Single-center retrospective cohort review
Setting: Academic tertiary referral center
Patients: All patients undergoing resection for Stage IIIA NSCLC were included. A total of 364 patients underwent surgery for Stage IIIA NSCLC during the study period (2006-2016). Median age was 64 years and 58.8% were female.
Interventions: Surgery included segmentectomy(6.6%), lobectomy(75.8%), bilobectomy(3.9%) or pneumonectomy(13.7%). Video-assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) and traditional open approaches were applied.
Main Outcome Measures: Perioperative outcomes, 5-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS)
Results: 246/364 patients underwent neoadjuvant therapy prior to surgery. 42 patients had induction chemotherapy and 204 patients underwent induction chemoradiation. OS was significantly better in patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy prior to resection (OS 47.6% vs 28.8%, p = 0.02, 95% CI). There was a non-significant trend toward improved DFS with induction therapy (30.8% vs 16.8%, p=0.059). Nodal downstaging was more common with an induction chemoradiation strategy (51.0% vs 33.3%, p=0.04). There were no significant differences in perioperative mortality or complications as a result of neoadjuvant therapy. VATS completion rates were significantly higher at the end of the study period compared to the beginning.
Conclusions: Survival following neoadjuvant therapy and surgery is favorable. Complication and mortality rates are low, even when resection requires pneumonectomy. VATS lobectomy is technically feasible in stage IIIA NSCLC with and without neoadjuvant therapy, and conversion rates can be expected to decrease over time. 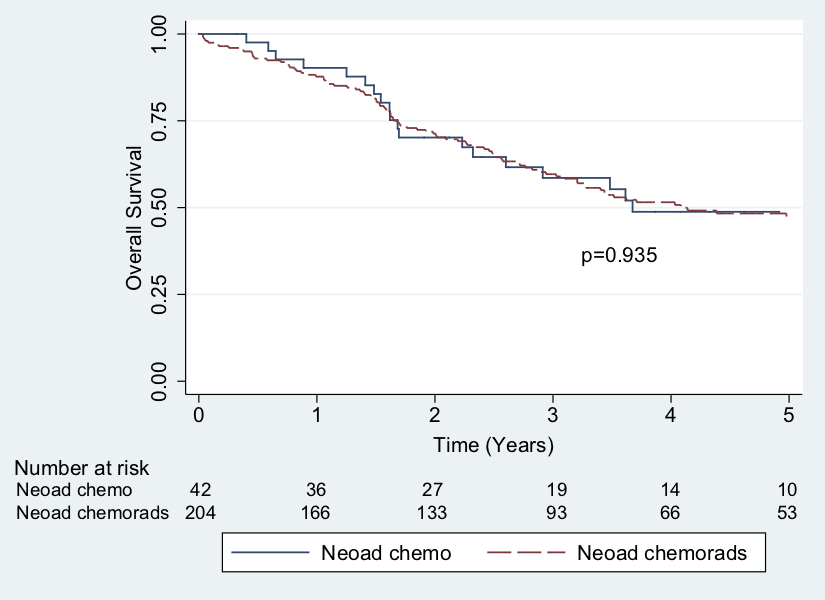
Back to 2019 Abstracts




