|
Back to 2011 Program
Tracheostomy Reduces Deadspace Ventilation
*Kartik Pandya, Virginia Eddy, *Steven Desjardins
Maine Medical Center, Portland, ME
Objective:
To document change in Vd/Vt in ventilated patients after a percutaneous tracheostomy using the single breath CO2 monitor.
Design:
A before-after trial on ventilated patents using single breath CO2 wave forms generated by the CO2 wave form monitor.
Setting:
The Intensive Care Unit (ICU) at a tertiary care referral hospital.
Patients:
One hundred and one consecutive ventilated patients in a mixed medical-surgical ICU were enrolled.
Interventions:
Ventilated patients underwent bedside percutaneous dilational tracheostomies by ICU attendings.
Main Outcome Measures:
A pre-, immediate post-, and three day post-tracheostomy single breath CO2 wave forms were measured using the CO2 wave form monitor. A power calculation was performed to show a standard ten percent difference between pre and post tracheostomy groups.
Results:
Average pre-tracheostomy Vd/Vt was 0.359 (SD of 0.128), immediate post-tracheostomy was 0.339 (SD of 0.128) and 3 days post was 0.404 (SD of 0.157). When the pre and immediate post Vd/Vt averages are compared the p-value is 0.029. 47 patients had Vd/Vt measurements 3 days post-tracheostomy; when they are compared to the immediate post the p-value is 0.006.
Conclusion:
Ours is the first adequately powered study to measure the change in Vd/Vt in pre and post tracheostomy patients. A reduction in the Vd/Vt measurement between the pre and immediate post-tracheostomy group was found. Further studies will be needed to explore the finding of increased Vd/Vt of the 47 patients who had data at 3 days. 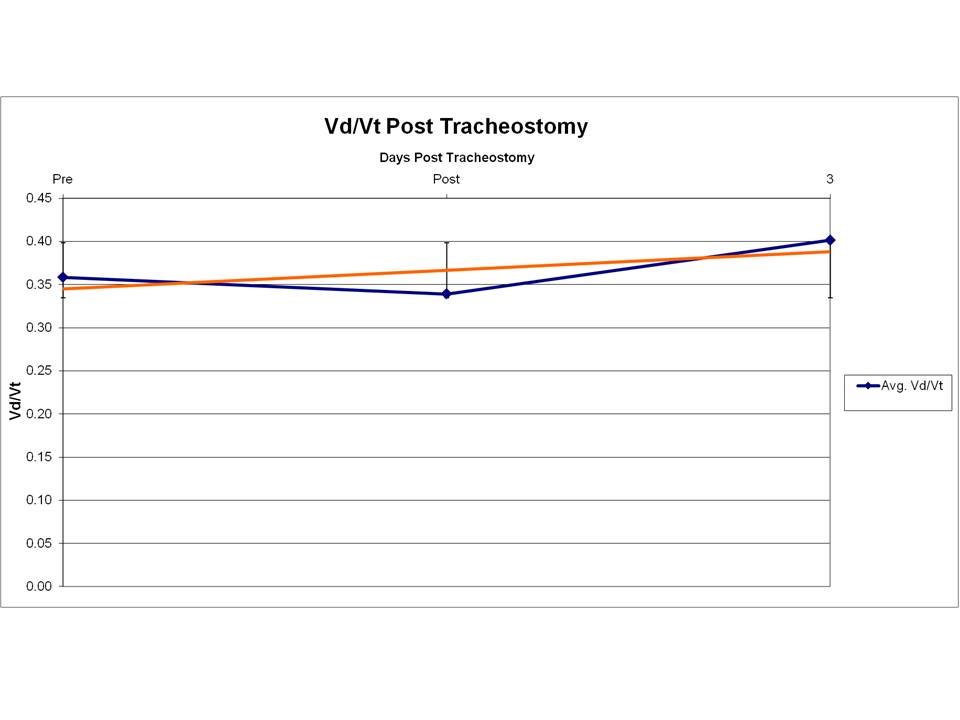
Back to 2011 Program
|
|
